About Product
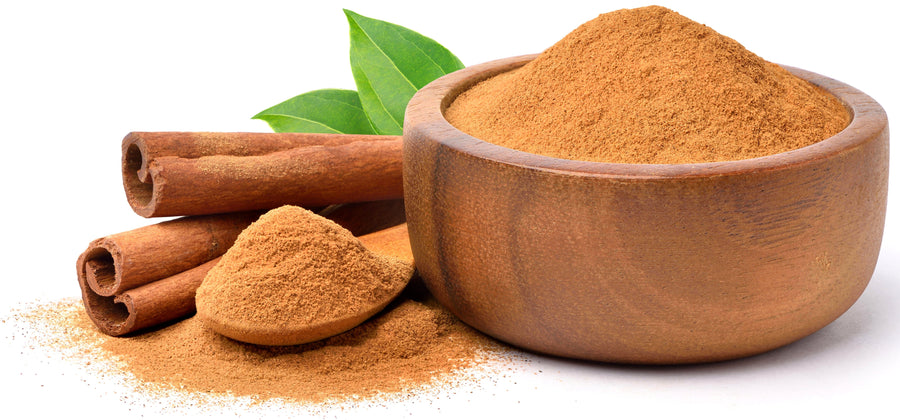
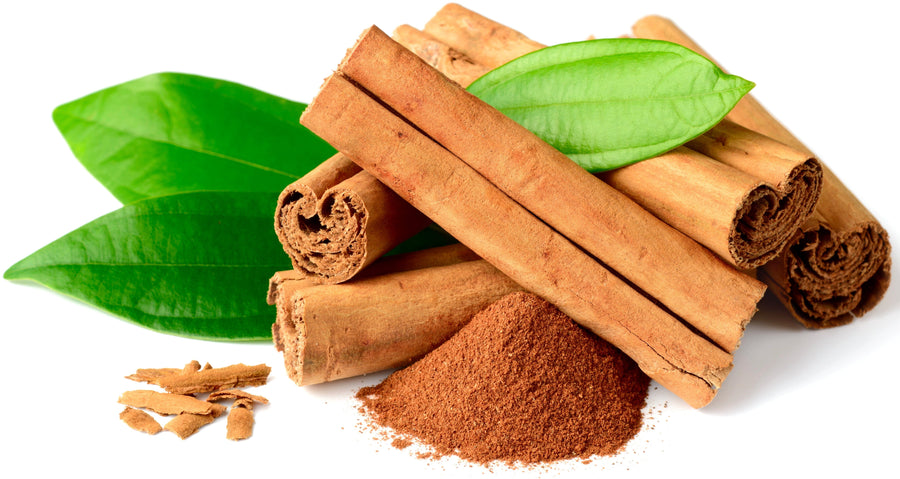
Cassia Cinnamon powder is derived from the inner bark of the cassia tree, which is native to Southeast Asia.
It has been used for centuries as a spice with unique properties and was first documented by the ancient Egyptians in 2000 B.C.
Throughout history, it has been used to support a wide range of issues and was highly valued in ancient Rome and China.
It was even used as a currency at one point! Today, cinnamon powder continues to be used in TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine) and as a flavoring agent in various dishes, from sweet desserts to savory main courses.
Its sweet, spicy flavor is a favorite for many, and its unique aroma is unmistakable.
Minerals: Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Zinc, Copper, Manganese, Selenium
-
Vitamins: Vitamin C, Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid, Vitamin B-6, Folate, Choline, Betaine, Beta carotene, Alpha Carotene, Cryptoxanthin-Beta, Lycopene, Vitamin A (I.U.), Lutein & Zeaxanthin, Vitamin E, Gamma Tocopherol, Delta Tocopherol, Vitamin K
-
Amino Acids: Tryptophan, Threonine, Isoleucine, Leucine Lysine, Methionine, Cystine, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Valine, Arginine, Histidine, Alanine, Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid, Proline, Serine
-
Flavonoids: Proanthocyanidin, 4-6 Mers, 7-10 Mers, Monomers, Dimers, Trimers
-
Essential Oils: Cinnamaldehyde
-
Phenols and Terpenes: Eugenol, Trans-Cinnamic acid, Hydroxycinnamaldehyde, o- Methoxycinnamaldehyde, Cinnamyl alcohol and its acetate, Limonene, Alpha-terpineol, oligomeric procyanidins
Suggested Use: Add a dash or more to recipes or drinks.
Other preparations:
Tincture:
-
This method can take 15 to 30 days.
-
You will need three items (a mason jar with a cover, the herb/herbs of your choice, and liquid for extracting).
-
The extracting liquid can be alcohol, alcohol/ water combo, vinegar, or vegetable glycerin.
-
Take the product and fill the jar ¾ full, add the liquid of your choice, and close the jar.
-
Then shake the jar so everything is well mixed.
-
Give the jar a good 5-minute shake several times a day.
-
After 15 to 30 days, strain and bottle in glass tincture jars.
Other Names: Indonesian Cinnamon, Padang Cassia, Korintje, Canela. Origin: Grown and harvested in Indonesia and packaged with care in Florida, USA.
How to Maintain Optimum Freshness
- This product is packaged in airtight stand-up, resealable foil pouches for optimum freshness.
- Once opened, push the air out of the pouch before resealing it to preserve maximum potency.
- Keep your powder in a cool, dark, dry place.
This product is 100% natural and minimally processed:
Taste, smell, texture, and color vary from batch to batch. Go here to learn why our products may naturally vary.
The important protections we take to bring you safe and nutritious superfoods:
Please go here to discover the essential steps we take to deliver fresh, quality nutrition.
Bulk Quantities?
Need to order a large quantity of our products? We are happy to help! Please get in touch with our Bulk department to discuss the details.
* Product packaging, pictures, and origin may vary.
Sources & References
1. Braun, R. et al. 1997. Standardzulassungen für Fertigarzneimittel"”Text and Kommentar. Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag
2. British Herbal Pharmacopoeia (BHP). 1996. Exeter, U.K.: British Herbal Medicine Association
3. Bruneton, J. 1995. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Medicinal Plants. Paris: Lavoisier Publishing
4. Der Marderosian, A. (ed.). 1999. The Review of Natural Products. St. Louis: Facts and Comparisons
5. Europäisches Arzneibuch, 3rd ed. (Ph.Eur.3). 1997. Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag
6. Grieve, M. 1979. A Modern Herbal. New York: Dover Publications, Inc.
7. The Homeopathic Pharmacopoeia of the United States (HPUS). 1992. Revision Service Official Compendium. Boston: Pharmacopoeia Convention of the American Institute of Homeopathy
8. Karnick, C.R. 1994. Pharmacopoeial Standards of Herbal Plants, Vol. 1. Delhi: Sri Satguru Publications. 94"“95
9. Leung, A.Y. and S. Foster. 1996. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
10. List, P.H. and L. Hörhammer (eds.). 1973. Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis, 4th ed. Vol. 4. New York: Springer Verlag. 54, 884
11. Hänsel, R., K. Keller, H. Rimpler, G. Schneider (eds.). 1992. Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis, 5th ed. Vol. 4. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer Verlag. 884
12. McGuffin, M., C. Hobbs, R. Upton, A. Goldberg. 1997. American Herbal Product Association's Botanical Safety Handbook. Boca Raton: CRC Press
13. Newall, C.A., L.A. Anderson, J.D. Phillipson. 1996. Herbal Medicines: A Guide for Health-Care Professionals. London: The Pharmaceutical Press
14. Wichtl, M. and N.G. Bisset (eds.). 1994. Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmaceuticals. Stuttgart: Medpharm Scientific Publishers
15. Akira, T., S. Tanaka, M. Tabata. 1986. Pharmacological studies on the antiulcerogenic activity of Chinese cinnamon. Planta Med 52(6):440"“443
16. Azumi, S., A. Tanimura, K. Tanamoto. 1997. A novel inhibitor of bacterial endotoxin derived from cinnamon bark. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 234(2):506"“510
17. Braun, R. et al. 1997. Standardzulassungen für Fertigarzneimittel"”Text and Kommentar. Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag
18. British Herbal Pharmacopoeia (BHP). 1983. Keighley, U.K.: British Herbal Medicine Association
19. Bruneton, J. 1995. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Medicinal Plants. Paris: Lavoisier Publishing
20. Chang, H.M. and P.P.H. But (eds.) 1986. Pharmacology and Applications of Chinese Materia Medica. Philadelphia: World Scientific. 510"“514
21. Grieve, M. 1979. A Modern Herbal. New York: Dover Publications, Inc.
22. Hänsel, R., K. Keller, H. Rimpler, G. Schneider (eds.). 1992. Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis, 5th ed. Vol. 4. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer Verlag
23. Hikino, H. 1985. Oriental Medicinal Plants. In: Wagner, H., H. Hikino, N.R. Farnsworth. 1985. Economic and Medicinal Plant Research, Vol. 1. London: Academic Press. 69"“70
24. Leung, A.Y. and S. Foster. 1996. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
25. List, P.H. and L. Hörhammer (eds.). 1973. Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis, Vol. 4. New York: Springer Verlag. 54, 884
26. McGuffin, M., C. Hobbs, R. Upton, A. Goldberg. 1997. American Herbal Product Association's Botanical Safety Handbook. Boca Raton: CRC Press
27. Nadkarni, K.M. 1976. Indian Materia Medica. Bombay: Popular Prakashan. 328"“330
28. Newall, C.A., L.A. Anderson, J.D. Phillipson. 1996. Herbal Medicines: A Guide for Health-Care Professionals. London: The Pharmaceutical Press
29. Tu, G. (ed.). 1992. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (English Edition 1992). Beijing: Guangdong Science and Technology Press. 31
30. Tyler, V.E., L.R. Brady, J.E. Robbers. 1988. Pharmacognosy , 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. 119"“122
31. Yen, K.Y. 1992. The Illustrated Chinese Materia Medica"” Crude and Prepared. Taipei: SMC Publishing, Inc.
32. http://www.naturalnews.com/045969_cinnamon_bark_Parkinsons_disease_Chinese_medicine.html
33. http://www.rush.edu/webapps/MEDREL/servlet/NewsRelease?id=1768
34. http://www.ibtimes.co.in/cinnamon-may-help-treat-parkinsons-disease-study-604144
35. http://www.naturalnews.com/043510_cinnamon_Alzheimers_disease_blood_pressure.html
36. http://www.naturalnews.com/031133_cinnamon_diabetes.html
37. http://science.naturalnews.com/cinnamon.html
38. Zhongshan Medical College Editorial Group (ZMC). 1975. Clinical Application of Chinese Traditional Drugs, 1st ed. Guangdong: Guangdong People's Publishing House. 8, 201
* Reviews & Success Stories Disclaimer
Product reviews solely reflect the views and opinions expressed by the contributors and not those of Z Natural Foods. Z Natural Foods does not verify or endorse any claims made in these reviews. Statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or health condition.REFERRAL PROGRAM
Share your personal link to your friends and welcome them with rewards. Claim yours when they make their first purchase.
GIVE
$10 off discount

GET
$10 off discount
Other products in the same category
Ultimate Superfood Fusion
$29.99
Beet Root Powder - Organic
$12.99





























































































